Macular degeneration is one of the leading causes of vision loss, particularly in adults over the age of 50. This progressive eye disease affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision, which is essential for tasks like reading, recognizing faces, and driving.
At Thind Eye Hospital, recognized as the best eye hospital in and around Jalandhar, our expert specialists provide advanced diagnosis and treatment to manage this condition effectively.
In this guide, we will explore the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and prevention tips to help you maintain clear vision and eye health.
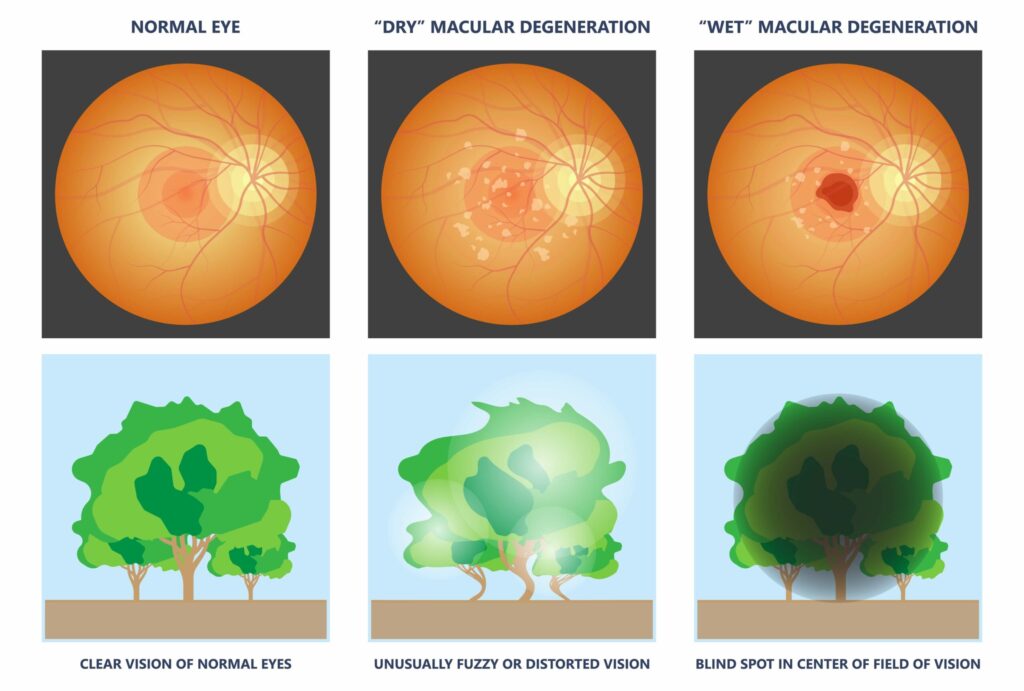
What Is Macular Degeneration?
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a retinal disease that gradually deteriorates the central vision. The condition typically progresses in two forms:
1. Dry Macular Degeneration (Non-Exudative)
- The most common type, affecting about 90% of AMD patients
- Occurs when light-sensitive cells in the macula break down
- This leads to gradual central vision loss
2. Wet Macular Degeneration (Exudative)
- Less common but more severe
- Caused by abnormal blood vessels leaking fluid into the retina
- Can cause sudden and significant vision loss
Both forms of macular degeneration can cause severe visual impairment, making early detection and treatment by a retina specialist crucial.
Common Risk Factors for Macular Degeneration
Several factors increase your risk of developing AMD, including:
1. Age (Primary Risk Factor)
- The likelihood of developing AMD increases significantly after age 50
2. Genetics & Family History
- If AMD runs in your family, you have a higher risk of developing the condition
3. Smoking
- Smokers are two to three times more likely to develop AMD
- Tobacco use damages retinal blood vessels, leading to faster degeneration
4. Poor Diet & Nutrition
- Diets low in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins contribute to retinal damage
- High consumption of processed foods and unhealthy fats increases the risk
5. Hypertension & Cardiovascular Disease
- High blood pressure restricts blood flow to the retina, accelerating vision loss
- Poor cardiovascular health also increases AMD risk
6. Prolonged UV Exposure
- Excessive UV radiation damages the retina over time
- Wearing UV-protective sunglasses reduces risk
7. Obesity & Sedentary Lifestyle
- Studies show that overweight individuals have a higher risk of AMD
- Lack of exercise contributes to poor circulation, affecting retinal health
8. Diabetes & Diabetic Eye Disease
- Diabetic patients are more likely to develop diabetic eye disease and AMD
- Diabetic retinopathy can worsen macular degeneration
If you have any of these risk factors, consult a specialist at Thind Eye Hospital for early screening and prevention strategies.
Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
AMD often develops gradually and painlessly, but early detection is essential. Common symptoms include:
- Blurry vision or difficulty reading
- Dark or blind spots in the center of the vision
- Straight lines appearing wavy or distorted
- Difficulty recognizing faces
- Increased sensitivity to glare
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule an eye exam immediately with a retina specialist at Thind Eye Hospital.
How to Prevent Macular Degeneration
While AMD has no definitive cure, several lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk and slow its progression.
1. Follow an Eye-Healthy Diet
A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins can help protect the retina. Include:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens) – High in lutein and zeaxanthin
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) – Rich in omega-3 fatty acids
- Nuts & seeds (walnuts, flaxseeds, almonds) – Reduce inflammation
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, berries) – High in vitamin C
- Carrots & sweet potatoes – Great source of vitamin A
2. Quit Smoking
- Reduces oxidative stress on retinal cells
- Improves blood circulation to the eyes
- Lowers the risk of wet macular degeneration
3. Control Blood Pressure & Heart Health
- Reduce sodium intake
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation
4. Wear UV-Protective Sunglasses
- Block harmful UV rays that accelerate retinal damage
- Choose sunglasses with 100% UVA & UVB protection
5. Exercise Regularly
- Improves blood circulation to the eyes
- Reduces risk of cardiovascular diseases affecting retinal health
6. Get Regular Eye Exams
- Early detection is key to managing AMD effectively
- Consult a retina specialist or macular degeneration specialist for comprehensive screenings
At Thind Eye Hospital, we offer advanced diagnostic tools to detect diseases in its early stages, ensuring timely intervention and treatment.
Treatment Options for Macular Degeneration
While there is no cure for AMD, several treatment options can help slow progression and improve vision quality.
1. Anti-VEGF Injections (For Wet AMD)
- Inhibits abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina
- Helps prevent vision loss and stabilize eyesight
2. Low Vision Aids
- Magnifying glasses, special lenses, and electronic aids help improve visual function
3. Laser Therapy
- Used in some cases of wet macular degeneration to seal leaking blood vessels
4. Cornea Transplant (In Severe Cases)
- Recommended for patients with severe retinal damage
Thind Eye Hospital specializes in vision loss treatment, diabetic eye disease management, and cornea transplant surgeries, providing cutting-edge care for AMD patients.
Protecting Your Vision for the Future
Macular degeneration is a serious eye disease that can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated. However, by understanding risk factors, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking regular eye check-ups, you can protect your vision for years to come.
At Thind Eye Hospital, our expert macular degeneration specialists and retina specialists provide advanced diagnostics and personalized treatment plans to help patients manage AMD effectively.


